Description of the rabbit
Rabbit breeding involves keeping animals of both sexes on the farm: both rabbits and rabbits. The rabbit is needed in order to reproduce offspring and feed newborn rabbits.
How to properly maintain and care for rabbits
If there are both females and males on the farm, the farmer is able to recreate the entire life cycle, from raising young animals to selling animals by live weight or as meat or fur. We will find out what the maintenance of rabbits and care for them should be in more detail.
Determination of the state of the hunt
The female must produce offspring, childbirth occurs after a successful mating. The mating will succeed only if the female is in a state of hunting. It is important to understand how to correctly identify this condition yourself.
The first thing worth paying attention to is the behavior of the animal and the condition of the female's genitals and nipples. The genital slit becomes edematous, acquires a red tint, white or bloody spotting appears. The nipples are swollen. The frequency of hunting in a rabbit is usually once a week (less often - a month), while this state lasts about 30-45 hours.
As for behavior, a young rabbit in heat becomes more restless, in some cases even aggressive, capable of injuring herself and her fellows. These signals are noted:
- Aggressive animals gnaw and scratch the cage bars with their paws for no reason, jump, snort, wheeze and sometimes even fight with other rabbits, causing them and themselves injuries.
- Plucks out fluff and hair on the body.
- You can see the hay in her teeth, which she carries from one place to another. This is how her maternal instinct manifests itself: a young rabbit thinks about how to equip a nest for future offspring.
- Appetite often deteriorates, the animal stops eating.
To understand and check whether the female is willing and ready for crawl coverage at the moment, a simple test can be carried out. For this, stroking movements are performed from the head towards the tailbone. If the eared one is waiting for a crawl, she will certainly raise her pelvis, thereby giving a signal for mating. You can also try to conduct a test mating, check how the rabbit will behave when the rabbit climbs on it.
To do this, a rabbit is placed in the cage and the female's reaction is observed. If the rabbit begins to behave aggressively, does not allow the male to approach her, it is better to postpone the mating.

Bitch rabbits
Why doesn't the rabbit hunt? If the state of hunting does not come, although the time has already come, you need to analyze and determine what may be wrong. The reasons for the lack of hunting are as follows:
- inappropriate conditions of detention;
- unbalanced diet;
- change in weather or climate;
- insufficient walking.
In order to accelerate the state of hunting, it is recommended to artificially lengthen the daylight hours, this is especially true in winter and autumn, when the air temperature is low, there is little sun and the animals walk less. If this is not done, do not expect frequent offspring from the rabbit.
How is a rabbit's pregnancy
How much does a domestic rabbit walk pregnant? Fostering lasts about a month, that is, after 30-40 days (rabbits walk around only in exceptional cases), rabbit offspring are born. Moreover, the number is the greater, the more cubs are in the womb of the mother. The same fact influences how quickly the animal crawls. If we analyze how quickly the cubs develop in the bosom of the mother, then by the middle of the term their weight is at least 2 g with an increase of 2-3 cm.
During pregnancy, the behavior of the rabbit changes, you can notice that she has become more cautious and even timid. Stress or fear can cause spontaneous miscarriage, and babies will be born prematurely.
During the pregnancy of a rabbit, it is important to pay due attention to her feeding. If the diet is not adjusted in time, there will be a possibility that she will not be able to feed the offspring enough, and her state of health will not be able to recover completely after birth, especially if the rabbit has it first.
For a pregnant female, it is necessary to create special conditions of detention: to transfer her from an ordinary cage to a special mother house, where a corner for childbirth will be equipped, as well as a place for a future nest. All items that will be in the mother liquor must go through mandatory sterilization so that the newborn rabbit does not catch any disease in a few days.
Nutrition of a pregnant rabbit
The menu of a rabbit carrying cubs should be varied and moderately high in calories. Usually the norm is 200-230 feed units. Moreover, for every 100 units, there is about 15-18 g of protein due to the presence of protein products. This component is extremely important for the life of a pregnant female rabbit, as it is involved in the formation of the fetus and placenta. Also, the diet should contain vitamins and all the necessary minerals.
After 10-14 days from the beginning of pregnancy, you need to revise the diet and exclude silage and all bulk feed from it. The best substitute would be a regular carrot, which rabbits eat with great pleasure. Immediately before childbirth, the menu may consist of the following products:
- Compound feed, legumes (about 25% of all dry feed), grain and oats.
- Sunflower meal, daily rate - about 60 g.
- Soybean meal - no more than 30 g.
- Boiled potatoes - about 100-150 g.
- Fresh carrots - no more than 150 g per day.
- Fresh grass or hay - 500 g or 150 g, respectively.
- Bone meal - 3-5 g per day.
- You need to give the animal salt - 1.5 g.
- Ground eggshell - about 3 g.
- Fish fat - no more than 2 g.
In winter, it is worth paying special attention to vitamins, since vegetables and fruits are too expensive a pleasure. At the same time, sprouted grains of oats or wheat can be added to the menu of the fledging female.

Diet of a pregnant rabbit
If the diet is not made correctly, for example, there is not enough sodium in it, there is a risk that after a while (a couple of days) the rabbit will eat her own newborn rabbits.
Pregnant rabbits do not need to be fed for slaughter. The fact is that overweight females are more likely to have a sick offspring - the female should not be allowed to become fat. Also, we must not forget to ensure that the animal has constant access to water, fill the drinking bowls on time and keep them clean: the rabbit should drink a lot.
Rabbit and litter care
Most often, during childbirth, a rabbit does not need help and stimulation from a person. Okrol usually occurs at night when the owner is not around. Next, a completely logical question arises: what to do next?
The first thing to take care of is the health of the little ones. It is required to examine the offspring, whether all the rabbits are alive, whether all are released from the intrauterine film. It is important not to delay the examination, since the newly-made mom is able to eat her babies.This can happen for several reasons: malnutrition, sodium deficiency in food. The worst reason: the rabbit eats stillborn pets, and at the same time accidentally eats those who were absolutely healthy.
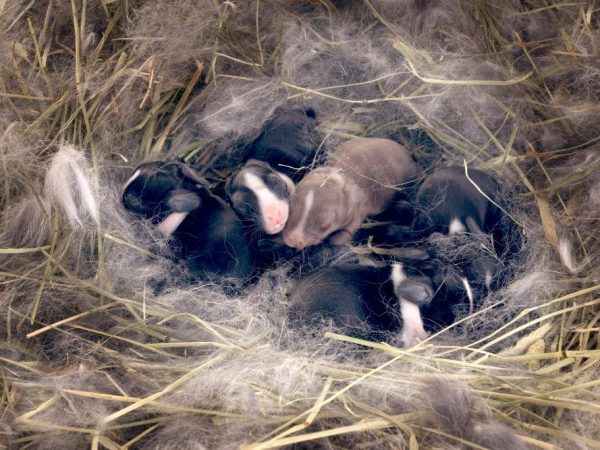

How is the birth of a rabbit
The owner must make sure that the rabbit feeds her offspring. If this does not happen, you should step in and start feeding the babies yourself. If the female responsibly feeds the cubs, they quickly recover and gain weight. This is due to the fact that the fat content of rabbit milk is high, because of this, the number of feedings is record low: only 2 times a day.
It happens that the rabbit flatly refuses to feed her offspring, it happens that milk is lost. If this happens, you can try to make a substitution: add the babies to another female who has an abundance of milk. However, first you need to make sure that the smell of the biological mother does not remain, otherwise the plan will not work.
Feeding during lactation
In order for the rabbit to be able to feed the offspring, it is necessary to provide her with normal nutrition, which will replenish all the calories spent on milk reproduction and direct feeding of the rabbits. How can the milkiness of a female rabbit be increased? It is still important to provide the animal with constant access to water, since the loss of fluid during lactation is colossal.
Until the rabbits are one month old, the daily diet of the rabbit should consist of 550-600 feed units, after which the figure increases to 750 units. At the same time, the protein content should not exceed 17-19 g for every hundred units.
What components should be included in the diet of a rabbit after giving birth? In the summer, there must be greens (grass) on the menu. This can be meadow grass, clover, oat harvests, and alfalfa. In winter, the green menu is replaced by quality hay and a variety of legumes. Here is an example of a daily menu for a rabbit in a state after birth:
- First-class hay or grass - 300 g or 1000 g, respectively.
- Sunflower cake - from 40 to 60 g.
- Sunflower meal - up to 40 g.
- Legumes (grains) and compound feed - up to 100 g per day.
- Yeast - up to 5 g.
- Bone flour - 2 to 8 g.
- Fish oil - about 5 g.
- Chalk - no more than 3 g.
- Salt - no more than 3 g.

Feeding during lactation
After jigging from the mother, the farmer will have to feed the babies until the time comes to resell or slaughter them. Feeding can be done starting from one month. For this, small grains are placed in the feeder for young animals. For safety, you can pre-pour boiling water over them to soften the product.
You should be careful about the presence of parsley and dill in the rabbit diet: their excess can cause the development of eating disorders. The same applies to fresh milk: when it is digested, a lot of gases are released, which can make the rabbit's belly swell.
Characteristic diseases of the rabbit
There are diseases that females are more susceptible to. One of these ailments is listeriosis - an infectious disease that is often fatal when the infection spreads enough through the blood. It is dangerous for humans, it is also tolerated by small rodents. Most often, feline rabbits suffer from listeriosis.
Along with listeriosis, infectious endometritis (inflammation of the lining of the uterus and its excessive proliferation), mastitis and other diseases affecting the genital organs of the female can develop.
Signs and symptoms appear suddenly against the background of the absolute health of the animal. Yesterday, a healthy, mobile and active rabbit suffers from a shaky gait, walks poorly and falls to her feet. Later, there is paralysis, multiple seizures and death. This is how listeriosis behaves in the acute stage.In this case, it is not possible to save the animal, therefore it is sometimes easier to slaughter the rabbit so as not to continue her suffering.
If the animal falls ill with a chronic form of listeriosis, there is a chance that the furry will survive. At the same time, the rabbits in the womb cannot be saved. The surviving rabbit will no longer be able to bear offspring, there will always be dead rabbits in the brood. Such rabbits should not be bred with males.


