Why does pear leaves turn brown
If the pear has brown leaves, the tree is sick. Such symptoms have a dangerous disease called bacterial cancer.
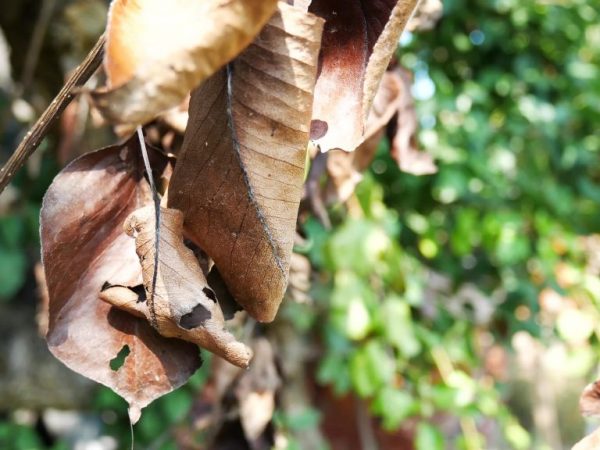

Why does pear leaves turn brown
Description of the disease
The causative agent of the disease is the bacterium Pseudomonas syringae.
In the spring, flowers dry up - this is the first symptom of the disease. According to the description, along with the inflorescences, the leaves located nearby are also affected. At first, they become covered with watery, yellow spots, which then turn brown. Holes with a diameter of 2-3 mm may form. Over time, the leaves and flowers turn black, but do not fall off - keep in this form until autumn.
Then spots of a pink-brown hue with a purple border appear on the branches. Inside the affected areas, the wood becomes blackish-brown, soft, and there is a smell of almonds. Cracks form, from which an orange liquid flows. After a while, thickenings form on the branches. On individual shoots, the bark dries up.
Fruits are affected less frequently. Bacterial cancer appears on them in the form of rotten brown spots, which after a while penetrate inside. Most often occur near the stalk.
Causes of occurrence
Pears are often affected by mechanical damage on the tree and through the buds at the tops. The causes of the disease can be different:
- grafting material in which harmful bacteria are stored;
- contaminated garden tools;
- insects and wind;
- cold and rain.
When bacteria enter the damaged area, they cannot heal on their own. New formations appear - tubercles - in which fungal spores multiply.
The causative agents of the disease hibernate in bark, wood, fruits, they begin to progress in spring, spread in wet weather, and feel good at temperatures of 2-30 ° C.
Effects
Bacterial cancer can cause great harm to trees. A large number of young branches or a whole tree die.
The plant loses turgor and winter hardiness, as a result of which new cracks and potholes are formed. They also contain fungi.
Disease prevention
To prevent bacterial cancer from damaging the plant, several measures are taken. Prevention is carried out in the spring and autumn.
- In the initial phase of leaf fall, the culture is sprayed with fungicides. Bacteria can easily penetrate into the place where the leaf has come off. The second treatment is carried out at the end of the fall.
- In the spring, preventive actions are used when bud swelling and flowering occur. Median 500 WP, Extra 350 SC, HOM are used at different times. The dose of the drug is determined strictly according to the instructions.
- In order to prevent the disease, varieties are planted that are resistant to the disease: August dew, Dukhmyanaya, Kudesnitsa, Memory of Yakovlev, Severyanka, Tikhonovka, Chizhovskaya.
- It is worth carrying out a systematic disinfection of garden tools. To do this, they are treated with a 5% formalin solution.
Bacterial cancer treatment
Folk remedies
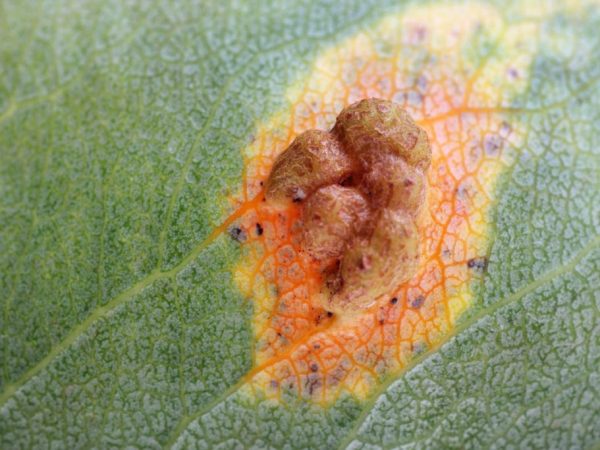
For minor lesions, folk remedies help
Folk remedies are effective in treating if the plant is slightly affected.
The following means are used:
- strong solution of potassium permanganate;
- sodium chloride solution plus a few drops of iodine;
- washing powder;
- diluted vodka.
Shoots and trunk of pears are treated with these substances. Particular attention is paid to damaged areas: they are abundantly moistened.
An organic putty made from mullein is also used. It is mixed with clay in a 1: 1 ratio.
Spraying is carried out with an ash-and-soap solution. To prepare it, take 300 g of wood ash and 3.5 liters of water, boil for 15 minutes, stirring. The volume is brought up to 10 liters and left for 2-3 hours. 30-40 g of liquid or crushed laundry soap is added to the filtered liquid. When processing until mid-summer, add 50 g of urea, after - 50 g of nitrophoska.
Chemicals
Spraying with Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate or azophos are considered effective.
Kresoxim-methyl and Vitaros can be isolated from new fungicides. The following are considered traditional:
- Raek - 1.5-2 ml per 10 liters of water. Apply up to 4 times: before bud swelling, before flowering, twice after flowering.
- Speed - 2 ml per 10 liters of water. Used before and after flowering.
- Strobes - 2 ml per 10 liters of water. Sprayed up to 3 times per season.
- Fitolavin - 20 ml per 10 liters of water. It is a complex of streptotricin antibiotics. Used up to 4 times per season.
Spraying rules
The pear is processed in 3 stages:
- during bud formation;
- when ¾ of the petals fall from the flowers;
- after harvest (the tree should already be without leaves).
Spraying is carried out together with pruning. In spring and autumn, damaged branches are removed, capturing a healthy part of them by a few centimeters. Places of cuts are disinfected with a 1% solution of ferrous sulfate (100 g per 10 l of water) and covered with garden varnish, into which a fungicide is added.
If the shoots are thick and cannot be cut, the damaged areas are trimmed to healthy wood. Then they are also covered with garden var. Leaves and fruits that turn brown should not be left on or composted. The removed shoots are burned. If the disease is neglected, the whole tree is removed and burned.
Biological agents
In the fight against bacterial cancer, the fungus antagonist Trichoderma is used. After removing the affected branches, the cut sites are covered with a suspension prepared on the basis of its spores. With this action, an antibiotic is produced, which prevents the disease from developing further.
In the treatment, a mixture of 5 strains of Pentaphage bacteriophages is used, which act against the causative agent of the disease. They either treat young shoots, or add them to putty from mullein and clay.
Conclusion
If the leaves and bark of the pear turn brown, this is a sign of bacterial cancer. The best solution is to start treatment immediately. In order to prevent the development of cancer, prevention is imperative.


